PID Control (Proportional+Integral+Derivative) Overview
P.I.D. Controller Overview
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PEED) management is that the most often used management algorithmic rule in business and has been universally accepted in industrial management. the recognition of inflammatory disease controllers are often attributed part to their strong performance in a very wide selection of in operation conditions and part to their practical simplicity, that permits engineers to control them in a very straightforward, simple manner. The inflammatory disease options found within the management loops of today’s managements have enabled America to realize a lot of bigger accuracy in our business control systems at a beautiful worth compared to it obtainable solely a couple of years agony.
PEED management could be a feedback mechanism that is employed on top of things system. because the name suggests, inflammatory disease algorithmic rule consists of 3 basic coefficients; proportional, integral and spinoff that area unit varied to induce best response. this sort of management is additionally termed as 3 term management. By dominant the 3 parameters – proportional, integral and spinoff we will bring home the bacon totally different management actions for specific work. inflammatory disease is taken into account to be the simplest controller within the system family.In every application, constant of those 3 actions area unit varied to induce best response and management. Controller input is error signal and output is given to the plant/process. signaling of controller is generated, in such how that, output of plant is attempt to bring home the bacon desired price.
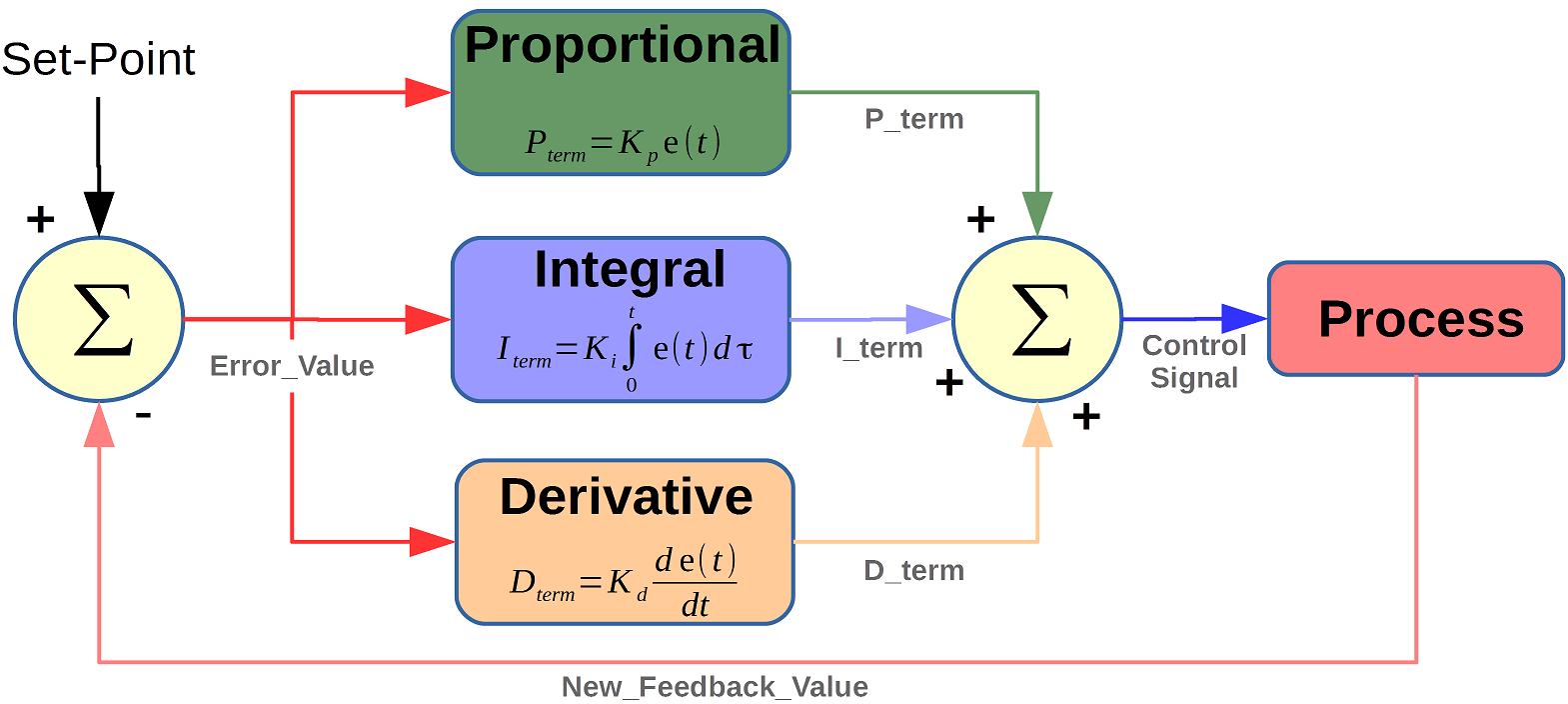
Figure : inflammatory disease controller diagram
For inflammatory disease management the activating signal consists of proportional error signal added with spinoff and integral of the error signal. Therefore, the activating signal for inflammatory disease management is
Working of inflammatory disease Controller
Manual management by Operator In manual management, the operator could sporadically browse the method variable (that must be controlled like temperature, flow, speed, etc.) and regulate the management variable (which is to be manipulated so as to bring management variable to prescribed limits like a constituent, flow valves, motor input, etc.). On the opposite hand, in automatic management, activity and adjustment area unit created mechanically on never-ending basis.All fashionable industrial controllers area unit of automatic sort (or closed-loop system controllers), that area unit sometimes created to provide one or combination of management actions. These management actions embody ON-OFF management, proportional management, proportional-integral management, proportional-derivative management and proportional-integral-derivative management.
With the employment of low value straightforward ON-OFF management solely 2 control states area unit attainable, like totally ON or totally OFF. it's used for restricted management application wherever these 2 management states area unit enough for management objective. but periodical nature of this management limits its usage and thus it's being replaced by inflammatory disease controllers.
PEED controller maintains the output such there's zero error between method variable and set point/ desired output by closed-loop system operations. inflammatory disease uses 3 basic management behaviors that area unit explained below.
proportional band is outlined because the quantity of amendment within the controlled variable needed to drive the loop output from zero to 100 percent.
Gain is that the quantitative relation of output amendment (%) over the measured variable amendment (%) that caused it.
Example: If the Pb is 2 hundredth, then the gain is five. a third amendment within the error signal (set point- method variable) can end in a V-J Day amendment in a very controller’s output, thanks to the proportional action. If gain is two, then the Pb is five hundredth.
P- Controller:
P-controller Proportional or P- controller provides output that is proportional to current error e (t). It compares desired or point with actual price or feedback method price. The ensuing error is increased with proportional constant to induce the output. If the error price is zero, then this controller output is zero.
This controller needs biasing or manual reset once used alone. this is often as a result of it ne'er reaches the steady state condition. It provides stable operation however continually maintains the steady state error. Speed of the response is enhanced once the proportional constant rate will increase.
P-Controller Response
I-Controller
Due to limitation of p-controller wherever there continually exists Associate in Nursing offset between the method variable and point, I-controller is required, that provides necessary action to eliminate the steady state error. It integrates the error over a amount of your time till error price reaches to zero. It holds the worth to final management device at that error becomes zero.
PI controller
Integral management decreases its output once negative error takes place. It limits the speed of response and affects stability of the system. Speed of the response is enhanced by decreasing integral gain Ki.
PI Controller Response
In higher than figure, because the gain of the I-controller decreases, steady state error conjointly goes on decreasing. for many of the cases, PI controller is employed notably wherever high speed response isn't needed.
While exploitation the PI controller, I-controller output is proscribed to somewhat vary to beat the integral land up conditions wherever integral output goes on increasing even at zero error state, thanks to solitariness within the plant.
D-Controller
I-controller doesn’t have the aptitude to predict the longer term behavior of error. thus it reacts unremarkable once the point is modified. D-controller overcomes this drawback by anticipating future behavior of the error. Its output depends on rate of amendment of error with regard to time, increased by spinoff constant. It provides the starter motor for the output thereby increasing system response.
PEED controller
In the higher than figure response of D controller is a lot of, compared to PI controller and conjointly sinking time of output is shriveled. It improves the steadiness of system by compensating section lag caused by I-controller. Increasing the spinoff gain will increase speed of response.
PEED Controller Response
So finally we have a tendency to discovered that by combining these 3 controllers, we will get the required response for the system. {different|totally totally different|completely different} manufactures styles different inflammatory disease algorithms.
Tuning ways of inflammatory disease Controller
Before the operating of inflammatory disease controller takes place, it should be tuned to suit with dynamics of the method to be controlled. Designers provide the default values for P, I and D terms and these values couldn’t provide the required performance and generally results in instability and slow management performances. differing kinds of standardization ways area unit developed to tune the inflammatory disease controllers and need a lot of attention from the operator to pick best values of proportional, integral and spinoff gains. a number of these area unit given below.
Trial and Error Method: it's a straightforward technique of inflammatory disease controller standardization. whereas system or controller is functioning, we will tune the controller. during this technique, 1st we've got to line Ki and Ks values to zero and increase proportional term (KP) till system reaches to periodical behavior. Once it's periodical, regulate Ki (Integral term) in order that oscillations stops and eventually regulate D to induce quick response.
Process reaction curve technique: it's Associate in Nursing open loop standardization technique. It produces response once a step input is applied to the system. Initially, we've got to use some management output to the system manually and ought to record response curve.
After that we'd like to calculate slope, dead time, rise time of the curve and eventually substitute these values in P, I and D equations to induce the gain values of inflammatory disease terms.
Process reaction curve
Ziegler-Nichols method: Ziegler-Nichols projected closed-loop system ways for standardization the inflammatory disease controller. Those area unit continuous athletics technique and damped oscillation technique. Procedures for each ways area unit same however oscillation behavior is totally different. In this, 1st we've got to line the p-controller constant, KP to a selected price whereas Ki and K values area unit zero. Proportional gain is enhanced until system oscillates at constant amplitude.
Gain at that system produces constant oscillations is named final gain (Koo) and amount of oscillations is named final amount (PC). Once it's reached, we will enter the values of P, I and D in inflammatory disease controller by Ziegler-Nichols table depends on the controller used like P, PI or PEED, as shown below.
PID Controller Structure
PID controller consists of 3 terms, specifically proportional, integral and spinoff management. The operation of those 3 managementlers provides management strategy for method control. inflammatory disease controller manipulates the method variables like pressure, speed, temperature, flow, etc. a number of the applications use inflammatory disease managementlers in cascade networks wherever 2 or a lot of PID’s area unit accustomed bring home the bacon control.
Above figure shows structure of inflammatory disease controller. It consists of a inflammatory disease block which provides its output to method block. Process/plant consists of ultimate management devices like actuators, management valves and alternative management devices to manage varied processes of industry/plant.
Feedback signal from the method plant is compared with a group purpose or reference signal u(t) and corresponding error signal e(t) is fed to the inflammatory disease algorithmic rule. in step with the proportional, integral and spinoff management calculations in algorithmic rule, the managementler produces combined response or controlled output that is applied to plant control devices.
All management applications don’t want all the 3 management components. combos like PI and atomic number 46 controls area unit fairly often utilized in sensible applications.
PID management represents a major advancement within the controls business. it's a awfully effective technique for providing precise management. though inflammatory disease management could be a comparatively complicated feature, management engineers and technicians can notice that well-designed product conjointly build it user friendly.
It is vital to grasp what inflammatory disease management will do for your operation and to be told the way to found out an efficient inflammatory disease management loop. whereas Associate in Nursing improper setup is probably going to end in redundant callbacks, a properly tuned inflammatory disease management loop can deliver satisfaction.
PEED management could be a feedback mechanism that is employed on top of things system. because the name suggests, inflammatory disease algorithmic rule consists of 3 basic coefficients; proportional, integral and spinoff that area unit varied to induce best response. this sort of management is additionally termed as 3 term management. By dominant the 3 parameters – proportional, integral and spinoff we will bring home the bacon totally different management actions for specific work. inflammatory disease is taken into account to be the simplest controller within the system family.In every application, constant of those 3 actions area unit varied to induce best response and management. Controller input is error signal and output is given to the plant/process. signaling of controller is generated, in such how that, output of plant is attempt to bring home the bacon desired price.
Figure : inflammatory disease controller diagram
For inflammatory disease management the activating signal consists of proportional error signal added with spinoff and integral of the error signal. Therefore, the activating signal for inflammatory disease management is
Working of inflammatory disease Controller
Manual management by Operator In manual management, the operator could sporadically browse the method variable (that must be controlled like temperature, flow, speed, etc.) and regulate the management variable (which is to be manipulated so as to bring management variable to prescribed limits like a constituent, flow valves, motor input, etc.). On the opposite hand, in automatic management, activity and adjustment area unit created mechanically on never-ending basis.All fashionable industrial controllers area unit of automatic sort (or closed-loop system controllers), that area unit sometimes created to provide one or combination of management actions. These management actions embody ON-OFF management, proportional management, proportional-integral management, proportional-derivative management and proportional-integral-derivative management.
With the employment of low value straightforward ON-OFF management solely 2 control states area unit attainable, like totally ON or totally OFF. it's used for restricted management application wherever these 2 management states area unit enough for management objective. but periodical nature of this management limits its usage and thus it's being replaced by inflammatory disease controllers.
PEED controller maintains the output such there's zero error between method variable and set point/ desired output by closed-loop system operations. inflammatory disease uses 3 basic management behaviors that area unit explained below.
proportional band is outlined because the quantity of amendment within the controlled variable needed to drive the loop output from zero to 100 percent.
Gain is that the quantitative relation of output amendment (%) over the measured variable amendment (%) that caused it.
Example: If the Pb is 2 hundredth, then the gain is five. a third amendment within the error signal (set point- method variable) can end in a V-J Day amendment in a very controller’s output, thanks to the proportional action. If gain is two, then the Pb is five hundredth.
P- Controller:
P-controller Proportional or P- controller provides output that is proportional to current error e (t). It compares desired or point with actual price or feedback method price. The ensuing error is increased with proportional constant to induce the output. If the error price is zero, then this controller output is zero.
This controller needs biasing or manual reset once used alone. this is often as a result of it ne'er reaches the steady state condition. It provides stable operation however continually maintains the steady state error. Speed of the response is enhanced once the proportional constant rate will increase.
P-Controller Response
I-Controller
Due to limitation of p-controller wherever there continually exists Associate in Nursing offset between the method variable and point, I-controller is required, that provides necessary action to eliminate the steady state error. It integrates the error over a amount of your time till error price reaches to zero. It holds the worth to final management device at that error becomes zero.
PI controller
Integral management decreases its output once negative error takes place. It limits the speed of response and affects stability of the system. Speed of the response is enhanced by decreasing integral gain Ki.
PI Controller Response
In higher than figure, because the gain of the I-controller decreases, steady state error conjointly goes on decreasing. for many of the cases, PI controller is employed notably wherever high speed response isn't needed.
While exploitation the PI controller, I-controller output is proscribed to somewhat vary to beat the integral land up conditions wherever integral output goes on increasing even at zero error state, thanks to solitariness within the plant.
D-Controller
I-controller doesn’t have the aptitude to predict the longer term behavior of error. thus it reacts unremarkable once the point is modified. D-controller overcomes this drawback by anticipating future behavior of the error. Its output depends on rate of amendment of error with regard to time, increased by spinoff constant. It provides the starter motor for the output thereby increasing system response.
PEED controller
In the higher than figure response of D controller is a lot of, compared to PI controller and conjointly sinking time of output is shriveled. It improves the steadiness of system by compensating section lag caused by I-controller. Increasing the spinoff gain will increase speed of response.
PEED Controller Response
So finally we have a tendency to discovered that by combining these 3 controllers, we will get the required response for the system. {different|totally totally different|completely different} manufactures styles different inflammatory disease algorithms.
Tuning ways of inflammatory disease Controller
Before the operating of inflammatory disease controller takes place, it should be tuned to suit with dynamics of the method to be controlled. Designers provide the default values for P, I and D terms and these values couldn’t provide the required performance and generally results in instability and slow management performances. differing kinds of standardization ways area unit developed to tune the inflammatory disease controllers and need a lot of attention from the operator to pick best values of proportional, integral and spinoff gains. a number of these area unit given below.
Trial and Error Method: it's a straightforward technique of inflammatory disease controller standardization. whereas system or controller is functioning, we will tune the controller. during this technique, 1st we've got to line Ki and Ks values to zero and increase proportional term (KP) till system reaches to periodical behavior. Once it's periodical, regulate Ki (Integral term) in order that oscillations stops and eventually regulate D to induce quick response.
Process reaction curve technique: it's Associate in Nursing open loop standardization technique. It produces response once a step input is applied to the system. Initially, we've got to use some management output to the system manually and ought to record response curve.
After that we'd like to calculate slope, dead time, rise time of the curve and eventually substitute these values in P, I and D equations to induce the gain values of inflammatory disease terms.
Process reaction curve
Ziegler-Nichols method: Ziegler-Nichols projected closed-loop system ways for standardization the inflammatory disease controller. Those area unit continuous athletics technique and damped oscillation technique. Procedures for each ways area unit same however oscillation behavior is totally different. In this, 1st we've got to line the p-controller constant, KP to a selected price whereas Ki and K values area unit zero. Proportional gain is enhanced until system oscillates at constant amplitude.
Gain at that system produces constant oscillations is named final gain (Koo) and amount of oscillations is named final amount (PC). Once it's reached, we will enter the values of P, I and D in inflammatory disease controller by Ziegler-Nichols table depends on the controller used like P, PI or PEED, as shown below.
PID Controller Structure
PID controller consists of 3 terms, specifically proportional, integral and spinoff management. The operation of those 3 managementlers provides management strategy for method control. inflammatory disease controller manipulates the method variables like pressure, speed, temperature, flow, etc. a number of the applications use inflammatory disease managementlers in cascade networks wherever 2 or a lot of PID’s area unit accustomed bring home the bacon control.
Above figure shows structure of inflammatory disease controller. It consists of a inflammatory disease block which provides its output to method block. Process/plant consists of ultimate management devices like actuators, management valves and alternative management devices to manage varied processes of industry/plant.
Feedback signal from the method plant is compared with a group purpose or reference signal u(t) and corresponding error signal e(t) is fed to the inflammatory disease algorithmic rule. in step with the proportional, integral and spinoff management calculations in algorithmic rule, the managementler produces combined response or controlled output that is applied to plant control devices.
All management applications don’t want all the 3 management components. combos like PI and atomic number 46 controls area unit fairly often utilized in sensible applications.
PID management represents a major advancement within the controls business. it's a awfully effective technique for providing precise management. though inflammatory disease management could be a comparatively complicated feature, management engineers and technicians can notice that well-designed product conjointly build it user friendly.
It is vital to grasp what inflammatory disease management will do for your operation and to be told the way to found out an efficient inflammatory disease management loop. whereas Associate in Nursing improper setup is probably going to end in redundant callbacks, a properly tuned inflammatory disease management loop can deliver satisfaction.









No comments